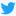


"Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death. He was crowned on 20 February at the age of nine. The son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour, Edward was the third monarch of the Tudor dynasty and England's first monarch raised as a Protestant. During Edward's reign, the realm was governed by a Regency Council because he never reached his majority. The Council was first led by his uncle Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset, (1547–1549), and then by John Dudley, 1st Earl of Warwick, from 1551 Duke of Northumberland.
Edward's reign was marked by economic problems and social unrest that, in 1549, erupted into riot and rebellion. An expensive war with Scotland, at first successful, ended with military withdrawal from Scotland as well as Boulogne-sur-Mer in exchange for peace. The transformation of the Church into a recognisably Protestant body also occurred under Edward, who took great interest in religious matters. Although his father, Henry VIII, had severed the link between the Church of England and Rome, Henry VIII had never permitted the renunciation of Catholic doctrine or ceremony. It was during Edward's reign that Protestantism was established for the first time in England with reforms that included the abolition of clerical celibacy and the Mass and the imposition of compulsory services in English. The architect of these reforms was Thomas Cranmer, Archbishop of Canterbury, whose Book of Common Prayer is still used.
In February 1553, at age 15, Edward fell ill. When his sickness was discovered to be terminal, he and his Council drew up a "Devise for the Succession", attempting to prevent the country's return to Catholicism. Edward named his first cousin once removed, Lady Jane Grey, as his heir and excluded his half-sisters, Mary and Elizabeth. However, this decision was disputed following Edward's death, and Jane was deposed by Mary within 13 days. As queen, Mary reversed Edward's Protestant reforms, which nonetheless became the basis of the Elizabethan Religious Settlement of 1559."
Wikipedia links:
Afrikaans,
Čeština, Dansk, Deutsch, Ελληνικά, English, Español, Eesti, Suomi, Français, עברית, Hrvatski, Magyar, Italiano, 日本語, 한국어, Nederlands, Norsk bokmål, Polski, Português, Română, Русский, Slovenčina, Svenska
other links:
http://www.britroyals.com/kings.asp?id=edward6
http://www.englishmonarchs.co.uk/tudor_6.htm
http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=1970
http://geneall.net/en/name/3073/edward-vi-king-of-england-and-ireland/
http://www.luminarium.org/encyclopedia/kingedward.htm
http://www.nndb.com/people/609/000093330/
http://www.tudorplace.com.ar/aboutEdward.htm
http://thepeerage.com/p10150.htm#i101497
EDWARD VI, King of England and Ireland, born at Greenwich on the 12th of October 1537, was the only child of Henry VIII by his third wife, Jane Seymour, who died of puerperal fever twelve days later. The story that the mother's life was deliberately sacrificed by the performance of Caesarean section is unfounded, although Jane's death was little noticed amid the rejoicings which greeted the advent of a male heir to the throne. But in spite of Holbein's vivacious portrait of Edward at the age of two (now at Hanover), he was a frail child, and a short life was anticipated for him from his early years. This did not prevent a strenuous education; until the age of six he was naturally left in the charge of women, but when he was only seven his tutor Dr Coxe, afterwards bishop of Ely, writes that he could decline any Latin noun and conjugate any regular verb (L. and P., 1544, ii. 726); "every day in the mass-time he readeth a portion of Solomon's Proverbs, wherein he delighteth much." Sir John Cheke, Sir Anthony Cooke and Roger Ascham all helped to teach him Latin, Greek and French; and by the age of thirteen he had read Aristotle's Ethics in the original and was himself translating Cicero's De philosophia into Greek.
Edward was Duke of Cornwall from his birth, but he was never prince of Wales, and he was only nine when he succeeded his father as king of England and Ireland and supreme head of the English church (28th of January 1546/7). His nonage threw power into the hands of Somerset and then of Northumberland, and enabled Gardiner and Bonner to maintain that the royal supremacy over the church was, or should be, in abeyance. Projects for his marriage were hardly even the occasion, but only the excuse, for Somerset's war on Scotland and Northumberland's subsequent alliance with France.
All factions sought to control his person, not because of his personality but because of his position; he was like the Great Seal, only more so, an indispensable adjunct to the wielder of authority. The Protector's brother [Edward's uncle, Thomas Seymour] tried to bribe him with pocket-money; Northumberland was more subtle and established a complete dominion over his mind, and then put him forward at the age of fourteen as entitled to all the power of Henry VIII. But he was only Northumberland's mask; of his individual influence on the course of history during his reign there is hardly a trace. A posthumous effort was made to give him the credit of a humane desire to save Joan Bocher from the flames; but he recorded with apparently cold-blooded indifference the execution of both his uncles, and he certainly made no attempt to mitigate the harassing attentions which the council paid his sister Mary. This passed for piety with the zealots, and the persecutions of Mary's reign reflected a halo on that of the Protestant Josiah. So strong was the regret that rumours of his survival persisted, and hare-brained youths were found to personate him throughout Mary's and even far into Elizabeth's reign.
Portrait of King Edward VI It was well that they were false, for Edward showed signs of all the Tudor obstinacy, and he was a fanatic into the bargain, as no other Tudor was except Mary. The combination would probably have involved England in disasters far greater than any that ensued upon his premature death; and it was much better that the Anglican settlement of religion should have been left to the compromising temper of Elizabeth. As it was, he bequeathed a legacy of woe; his health began to fail in 1552, and in May 1553 it was known that he was dying. But his will and the various drafts of it only betray the agitated and illogical efforts of Northumberland to contrive some means whereby he might continue to control the government and prevent the administration of justice.
Mary and Elizabeth were to be excluded from the throne, as not sufficiently pliant instruments; Mary Stuart was ignored as being under Scottish, Catholic and French influence; the duchess of Suffolk, Lady Jane Grey's mother, was excluded because she was married, and the duke her husband might claim the crown matrimonial. In fact, all females were excluded, except Jane, on the ground that no woman could reign; even she was excluded in the first draft, and the crown was left to "the Lady Jane's heirs male." But this draft was manipulated so as to read "the Lady Jane and her heirs male." That Edward himself was responsible for these delirious provisions is improbable. But he had been so impregnated with the divine right of kings and the divine truth of Protestantism that he thought he was entitled and bound to override the succession as established by law and exclude a Catholic from the throne; and his last recorded words were vehement injunctions to Cranmer to sign the will.
He died at Greenwich on the 6th of July 1553, and was buried in Henry VII's chapel by Cranmer with Protestant rites on the 8th of August, while Mary had Mass said for his soul in the Tower.
The Family of Edward VI
| 1537 |
October 12, 1537
|
Hampton Court Palace, Richmond, England
|
|
|
October 15, 1537
|
|||
| 1547 |
February 22, 1547
Age 9
|
Westminster Abbey, London,England
|
|
| 1553 |
July 6, 1553
Age 15
|
Greenwich Palace, London, England
|
|
|
August 8, 1553
Age 15
|
Henry VII Lady Chapel, Westminster Abbey, London, England
|