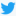




Emily "Mickey" Hahn authored fifty-two books and hundreds of articles. She published nearly 200 articles in The New Yorker magazine alone, and is (2011) best known for her novels The Song Sisters (1941) and China and Me (1944).
Emily Hahn became a successful writer during the 1930s due in some small part to poet Mitchell Dawson having submitted a few of her letters to The New Yorker. Mitchell Dawson had married Emily's sister Rose in 1921.
<><><><><><><><><><><><><><><><><><>
Emily Hahn (Chinese: 項美麗, January 14, 1905 - February 18, 1997) was an American journalist and author. Called "a forgotten American literary treasure" by The New Yorker magazine, she was the author of 52 books and more than 180 articles and stories. Her writings in the 20th century played a significant role in opening up Asia to the west.
Contents
One of six children of a dry goods salesman and a free-thinking mother, Emily Hahn was born in St. Louis, Missouri on January 14, 1905. Nicknamed "Mickey," she moved with her family to Chicago, Illinois when she was 15. In her memoir No Hurry to Get Home, she describes how being prevented from taking a chemistry class in which she was interested caused her to switch her course of study from English to Engineering at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. In 1926 she was the first woman to receive a degree there in Mining Engineering—despite the coolness of the administration and most of her male classmates. It was a testament to her intelligence and persistence that her lab partner grudgingly admitted, "you ain't so dumb!"
After graduation she worked briefly for an engineering company in Illinois, before traveling 2,400 miles (3,900 km) across the United States by car with a female friend, both disguised as men, and then working as a "Harvey Girl" tour guide in New Mexico. Later she traveled to the Belgian Congo, where she worked for the Red Cross, and lived with a pygmy tribe for two years, before crossing Central Africa alone on foot.
Her first book, Seductio ad Absurdum: The Principles and Practices of Seduction--A Beginner's Handbook (1930), was a tongue-in-cheek exploration of how men court women.
Her years in Shanghai, China (from 1935 to the Japanese invasion of Hong Kong in 1941) were the most tumultuous of her life. There she became involved with prominent Shanghai figures, such as the wealthy Sir Victor Sassoon, and was in the habit of taking her pet gibbon, Mr. Mills, with her to dinner parties, dressed in a diaper and a minute dinner jacket.
Supporting herself as a writer for The New Yorker, she lived in an apartment in Shanghai's red light district, and became romantically involved with the Chinese poet and publisher Sinmay Zau (traditional Chinese: 邵洵美; pinyin: Shao Xunmei). He gave her the entrée that enabled her to write a biography of the famous Soong sisters, one of whom was married to Sun Yat-sen and another to Chiang Kai-shek.
Hahn frequently visited Sinmay's house, which was highly unconventional for a Western woman in the 1930s. The Treaty of the Bogue was in full effect, and Shanghai was a city divided by Chinese and Westerners at the time. Sinmay introduced her to the practice of smoking opium, to which she became addicted. She later wrote, "Though I had always wanted to be an opium addict, I can't claim that as the reason I went to China."
After moving to Hong Kong, she began an affair with Charles Boxer,[1][2] the local head of British army intelligence. According to a December 1944 Time article, Hahn "decided that she needed the steadying influence of a baby, but doubted if she could have one. 'Nonsense!' said the unhappily-married Major Charles Boxer, 'I'll let you have one!' Carola Militia Boxer was born in Hong Kong on October 17, 1941".
When the Japanese marched into Hong Kong a few weeks later Boxer was imprisoned in a POW camp, and Hahn was brought in for questioning. "Why?" screamed the Japanese Chief of Gendarmes, "why ... you have baby with Major Boxer?" "Because I'm a bad girl," she quipped. Fortunately for her, the Japanese respected Boxer's record of wily diplomacy.
As Hahn recounted in her book China to Me (1944), she was forced to give Japanese officials English lessons in return for food, and once slapped the Japanese Chief of Intelligence in the face. He came back to see her the day before she was repatriated in 1943 and slapped her back.
China to Me was an instant hit with the public. According to Roger Angell of The New Yorker, Hahn "was, in truth, something rare: a woman deeply, almost domestically, at home in the world. Driven by curiosity and energy, she went there and did that, and then wrote about it without fuss."[3]
In 1945 she married Boxer who, during the time he was interned by the Japanese, had been reported by American news media to have been beheaded; their reunion—whose love story had been reported faithfully in Hahn's published letters—made headlines throughout the United States. They settled in Dorset, England at "Conygar", the 48-acre (190,000 m2) estate Boxer had inherited, and in 1948 had a second daughter, Amanda Boxer (now a stage and television actress in London).
Finding family life too constraining, however, in 1950 Hahn took an apartment in New York City, and visited her husband and children from time to time in England. She continued to write articles for The New Yorker, as well as biographies of Aphra Behn, James Brooke, Fanny Burney, Chiang Kai-Shek, D. H. Lawrence and Mabel Dodge Luhan. According to biographer Ken Cuthbertson, while her books were favorably reviewed, "her versatility, which enabled her to write authoritatively on almost any subject, befuddled her publishers who seemed at a loss as to how to promote or market an Emily Hahn book. She did not fit into any of the usual categories" because she "moved effortlessly ... from genre to genre."
In 1978 she published Look Who's Talking, which dealt with the controversial subject of animal-human communication (her personal favorite among her non-fiction books); she wrote her last book Eve and the Apes in 1988 when she was in her eighties.
Hahn reportedly went into her office at The New Yorker daily, until just a few months before she died on February 18, 1997 at the age of 92, following complications from surgery for a shattered femur.
"Chances are, your grandmother didn't smoke cigars and let you hold wild role-playing parties in her apartment", said her granddaughter Alfia Vecchio Wallace in her affectionate eulogy of Hahn. "Chances are that she didn't teach you Swahili obscenities. Chances are that when she took you to the zoo, she didn't start whooping passionately at the top her lungs as you passed the gibbon cage. Sadly for you ... your grandmother was not Emily Hahn."
In 1998, Canadian author Ken Cuthbertson published the biography Nobody Said Not to Go: The Life, Loves, and Adventures of Emily Hahn. "Nobody said not to go" was one of her characteristic phrases.
In 2005 Xiang Meili (the name given to Hahn by Sinmay) was published in China. It looks back at the life and loves of Hahn in the Shanghai of the 1930s.
Ken Cuthbertson, Nobody Said Not to Go: The Life, Loves, and Adventures of Emily Hahn (Boston: Faber and Faber, 1998). ISBN 057119950X
1. ^ asjapan.org
2. ^ plumsite
3. ^ [Private Angell, Roger] (2006). ''Let Me Finish''. Harcourt. p. 242. ISBN 9780151013500.
Source: Downloaded April 2011 from Wikipedia at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emily_Hahn
<> <><> <><><><><> <><> <>
Biographical Note
Hahn was born in St. Louis and lived there until her family moved to Chicago during her high school years. She later attended the University of Wisconsin and in 1926 received the first mining engineering degree awarded to a female student. Following graduation, until the spring of 1927, she worked for an engineering firm in St. Louis and then as a company courier for that firm in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Returning to the East during the summer, she attended Columbia University for graduate work, taught geology during the 1927/28 academic year, and then headed for Europe on her first overseas tour. After living in Florence and London, she returned home briefly in 1929 before going to the Congo and two years' residence there. In 1932 she began further travels, finally settling in Shanghai in 1935 where she taught English for three years.
All during this decade of travel and adventure Hahn wrote almost continually - articles, stories, letters - and many of her pieces were printed in The New Yorker, as well as five full-length books being published. The Sino-Japanese conflict eventually caused Hahn to leave Shanghai for Hong Kong, where she was later forced to remain after the Japanese took over that area in 1941. She was finally repatriated in 1943 and proceeded to produce two books concerning those years: China to Me and Hong Kong Holiday. In 1945 Hahn married British Major Charles Ralph Boxer, 1904-2000, whom she had met in Hong Kong prior to his internment as a POW, and following the war they moved to his family home in England. She continued to write short fiction, articles for magazine publication, particularly The New Yorker, and a remarkable number of books. During the 1950's she ventured into the juvenile field with some fiction, juvenile biographies, and descriptions of some of the countries in which she had traveled or lived. Other publications include biographies of Aphra Behn, James Brooke, Fanny Burney, Chiang kai-shek, D.H. Lawrence, and Mabel Dodge Luhan; a description of the diamond business; four books on zoos and animals; histories of China, Ireland, women; and several autobiographical accounts.
Source: Emily "Mickey" Hahn Papers at the Lilly Library (Public Services Department), Indiana University, Bloomington, IN 47405. Telephone (812) 855-2452. http://webapp1.dlib.indiana.edu/
<> <><> <><><><><> <><> <>
<> <><> <><><><><> <><> <>
<> <><> <><><><><> <><> <>
<> <><> <><><><><> <><> <>
| 1905 |
January 14, 1905
|
St Louis, Missouri, United States
|
|
| 1997 |
February 18, 1997
Age 92
|
Saint Vincent's Catholic Medical Center, 203 West 12th Street, Manhattan, New York County, New York, United States
|
|
| ???? |
University of Wisconsin
|