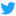 Follow Us
Follow Us Like Us
Like Us
public profile

Magnentius
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to: navigation, search
Flavius Magnus Magnentius
usurper of the Roman Empire
Although Magnentius restored certain rights to the Pagans, the reverse of this coin bears a prominent Christian chi-rho.
Reign January 18, 350 – August 11, 353
Born 303
Birthplace Samarobriva, Gaul
Died August 11, 353 (aged 50)
Place of death Mons Seleucus
Predecessor Constans
Successor Constantius II
Wife Justina
Flavius Magnus Magnentius (303–August 11, 353) was a usurper of the Roman Empire (January 18, 350 – August 11, 353).
Contents [hide]
1 Early life and career
2 Usurper
3 Demise
4 Notes
5 References
6 External links
[edit] Early life and career
Born in Samarobriva (Amiens), Gaul, Magnentius was the commander of the Herculians and Iovians, the imperial guard units[1]. When the army grew dissatisfied with the behaviour of Roman Emperor Constans, it elevated Magnentius at Autun on January 18, 350. Constans was abandoned by all except a handful of retainers, and he was slain shortly afterwards by a troop of light cavalry near the Pyrenees.
[edit] Usurper
Magnentius quickly attracted the loyalty of the provinces in Britannia, Gaul, and Hispania, in part because he proved to be far more tolerant towards both Christians and Pagans. His control on Italia and Africa was applied through the election of his men to the most important offices. However, the short-lived revolt of Nepotianus, a member of the Constantinian dynasty, showed Magnentius that his status of Emperor was to be consolidated against the members of that dynasty.
The self-proclaimed emperor tried to strengthen his grasp on the territories previously controlled by Constans, moving towards the Danube. Vetranio, commander of the Pannonian army, had been elected Augustus by his troops in Mursa on 1 March. This revolt had a loyalist mark, since Vetranio was supported by Constantina, and Constantius II himself recognized Vetranio, sending him the imperial diadem.
[edit] Demise
The remaining emperor of the family of Constantine I, Constantius II broke off his war in Syria with Persia, and marched west. Despite Magnentius' efforts to gain Vetranio to his cause, the old general reached Constantius with his army, and resigned the crown.
After electing Magnus Decentius (probably his brother) to Caesar and gathering as many troops as possible, the armies of Magnentius and Constantius met in the Battle of Mursa Major in 351; Magnentius led his troops into battle, while Constantius spent the day of battle praying in a nearby church. Despite Magnentius' heroism, his troops were defeated and forced to retreat back to Gaul.
As a result of Magnentius' defeat, Italy ejected his garrisons and rejoined the loyalist cause. Magnentius made a final stand in 353 in the Battle of Mons Seleucus, after which he committed suicide by falling on his sword.
Following the suppression of Magnentius' rebellion, Constantius commanded an investigation be made to find his followers. The most notorious agent in this search was the primicerius notariorum Paulus Catena.
Some sources state that Magnentius' father was a Briton and his mother a Frank.[2]
| 303 |
303
|
Samarobriva, Gaul
|
|
| 353 |
August 11, 353
Age 50
|
Mons Selencus
|