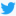


Grand Duke George Alexandrovich was the third son of Emperor Alexander III and Empress Marie of Russia. At times he was referred to by his relatives as "weeping willow" and was a much beloved member of the imperial family.
George was named after his mother's elder brother, King George I of Greece. As an infant, he was stronger and healthier than his brother Nicholas. He could be described as a typical Romanov. George was tall, unlike his elder brother Nicholas, handsome and full of fun. He was always getting into mischief and, because his mother had a great weakness for him, getting away with it. Like his siblings, he was brought up in a spartan fashion in the English manner. They slept on camp beds, rose at six and took a cold bath, although occasionally they were allowed to take a warm bath in their mother's bathroom. Breakfast was usually porridge and black bread; mutton cutlets or roast beef with peas and baked potatoes were served for lunch; bread, butter and jam at tea-time. Cake was a special treat. Nicholas and George had a sitting-room, dining-room, play-room and bedroom, all simply furnished. The only trace of ostentation was an icon surrounded by pearls and precious stones. George's mother taught him that family life was important. Because of his parents' happy marriage, he was brought up in an atmosphere of love and security missing in many royal households. On 27 May 1883, George's parents were crowned in a magnificent ceremony in the Uspensky Cathedral in the Kremlin in Moscow. The Emperor and Empress received the homage of the Imperial Family, including their sons, Nicholas and George, both in uniform. It was a major occasion in the life of the young Grand Duke. The family lived mostly in the security of the palace at Gatchina.
George was considered to be the cleverest of the Imperial children. He was also outgoing, like his mother. George and Nicholas shared the same tutors, but studied in adjoining rooms. They followed the course of the Academy of the Russian General Staff. Their tutors were distinguished professors. Their English teacher, Charles Heath, had once been tutor to their uncles, Grand Dukes Sergei and Pavel. Both brothers spoke and wrote faultless English. From Mr. Heath they acquired a love of sport, particularly shooting and fly-fishing. They also spoke fluent French and passable German and Danish. George displayed signs of a promising career in the Navy before falling ill with tuberculosis in 1890.
The Emperor and Empress both decided to send Nicholas and George on a nine-month-long trip to Japan in 1890. George would go as a naval cadet and Nicholas to complete his education by seeing something of the world. Their mother hoped the warm sun and the sea air would improve George's health. They left Gatchina on 4 November 1890. The Empress had never been separated from her sons for such a long time and she missed them terribly. "You cannot imagine how sad and hard it is to be without you, my angel, and how dreadfully it hurts to think of this long separation", she wrote sadly. Nicholas and George first went by warship to Athens where they were joined by their cousin, Prince George of Greece, known as "Greek Georgie". From there, they traveled to Egypt. From Bombay in India, Nicholas telegraphed that his brother George had to remain on ship because he had trouble with his leg. Although George assured his parents that he was perfectly well, they were suddenly informed he had a fever and would have to return home. The Empress was alarmed. "You can't imagine in what anguish I have passed these last few days", she wrote. "In spite of all the reasoning ... I had to take things calmly, and to tell myself that it ... is only this horrible malaria that will pass with a change of air ..." George, in fact, had acute bronchitis and was sent back to Athens where he could be examined by the Imperial doctors. The Empress was distressed for both brothers: George, whose disappointment she felt deeply and Nicholas, who was now deprived of his brother's company.
In November 1894, Alexander III died and Nicholas mounted the throne as Emperor. At the time, Nicholas had no children, thus according to the laws of succession of the Russian Empire, the Grand Duke George became Tsarevich (formally Tsesarevich, denoting the heir presumptive or heir apparent to the throne as opposed to any son of the Tsar, although the latter title fell into disuse in 1721 and was gradually supplanted by the more specific use of Tsarevich). George's ill-health had forced him to relocate to Likani. It was impossible for him to return to St. Petersburg for the funeral of his father, Alexander III. The doctors had forbidden it. Nicholas wrote to his brother, "... constantly pray to God to send you a full and speedy recovery, and to comfort you, because it is so much more difficult to be alone after such great sorrow than it is for us who are at least together!" George also missed the christenings of Nicholas' elder daughters, Olga and Tatiana. Shortly after the birth of Nicholas' third daughter, Maria, in June 1899, George wrote to his brother, "I am terribly sad that I have not yet been able to see your daughters and get to know them; but what can I do! It means it's not my fate, and everything is the will of God."
Visits from his mother to Likani were greatly enjoyable. In 1895, George and his mother visited Denmark. They had not seen their Danish relatives for four years. It was sad as it was the first time for both of them without the late Tsar. Then suddenly, his health deteriorated, "Yesterday, in the garden, he expectorated some blood...that frightened me more than I can tell - the surprise of it was shocking, because he had been so well of late...I am quite desperate that this should have happened here" As a result, George was forbidden to smoke and confined to bed until he was fit enough to return to Likani. Writing to Nicholas back home once again, George said about his trip to Denmark, "Of course it was good to see the family after 4 years, but it did not really do me any good, as I lost more than 5 pounds which I had put on with such difficulty in May and June. I also get out of breath more easily. So these are the results of my trip. Very annoying."
George died suddenly in Abastumani, on 9 August 1899, at the age of 28. He had been out alone on his motorcycle and some hours later, when he failed to return, his worried staff sent out a search party. By the time they found him it was too late. A peasant woman had discovered him collapsed at the side of the road, blood oozing from his mouth as he struggled to breathe. She supported him in her arms until he died.
The news reached Nicholas by telegram and he had the difficult task of telling his mother. She broke down and wept. He had seldom been out of her thoughts for the last few years and his death came as a terrible shock. His family were completely devastated. Nicholas was especially grief-stricken at losing his younger brother and childhood playmate. Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich wrote, "Everyone was struck, as if by lightning, by this sad and unexpected news. Queen Victoria wrote to Nicholas II, "Pray accept the expression of my sincerest sympathy in this great sorrow, for I know the affection you had for your poor brother Georgy, whose life was so sad and lonely." The Dowager Empress telegraphed Queen Victoria, "Thank you so much for kind sympathy in this terrible sudden bereavement... My poor dearest son died quite alone. Am heartbroken."
On 14 August 1899, he was laid to rest in the St. Peter and Paul Cathedral in Saint Petersburg, not far from his late father, Alexander III. During the service, his mother stood without tears, only deep suffering was imprinted on her face. When the coffin was put down into the tomb, Maria Feodorovna stood next to Xenia, holding her arm-in-arm and suddenly, looking at her daughter with widely open, unseeing eyes, she loudly said, "Let's go home. Let's go home, I cannot stand it anymore!" and she rushed out. When a board was laid down for leaving the tomb, she went away so quickly that it was difficult for others to keep pace with her. Nobody even had enough time to throw flowers on to the tomb. In the carriage she sobbed for a long time, pressing to her breast George's hat that she took off the coffin's cover.
Nicholas II always remembered George and his wonderful sense of humour. He would tell great jokes that amused his brother very much. Nicholas would dutifully write out the best jokes on pieces of paper and save them in a box. Years later, the Tsar would be heard laughing by himself in his room, looking through his old box of George's jokes. George's title as Heir Presumptive was passed to his younger brother, Michael, until the birth, in 1904, of Nicholas' son, Alexei. In 1910, Michael named his newborn son, George, after his late brother. This George would also die young; he was killed in a car crash in 1931 at the age of 20.
Decades later his body was disinterred from the grave in the Cathedral of St. Peter and Paul in St. Petersburg so that a sample of DNA could be taken from the remains to see whether skeletal remains allegedly belonging to his older brother, the last Tsar of Russia, Nicholas II, were legitimate or not. The DNA sample obtained from the Grand Duke's remains indicated that he was closely related to the DNA sample from the presumed remains of Nicholas II, confirming their identity. After the completion of DNA testing, the remains of Grand Duke George Alexandrovich were once again laid to rest not far from those of his older brother and family.
Великий князь Гео́ргий Алекса́ндрович (27 апреля (9 мая) 1871, Царское Село — 28 июня (10 июля) 1899 близ Абастумани, Тифлисская губерния) — третий сын Александра III и Марии Фёдоровны, младший брат Николая II. После 1894 года как первый в очереди на наследование российского престола носил титул цесаревича.
Детство
В детстве Георгий был более здоровым и сильным, чем его старший брат Николай. Он рос высоким, красивым, жизнерадостным ребёнком. Несмотря на то, что Георгий был любимчиком матери, он, как и другие братья, воспитывался в спартанских условиях. Дети спали на армейских кроватях, вставали в 6 часов и принимали холодную ванну. На завтрак им, как правило, подавали кашу и чёрный хлеб; на обед котлеты из баранины и ростбиф с горошком и запечённым картофелем. В распоряжении детей были гостиная, столовая, игровая комната и спальня, обставленные самой простой мебелью. Богатой была только икона, украшенная драгоценными камнями и жемчугом. Семья жила в основном в Гатчинском дворце.
В 11 лет его высекли по голым ягодицам, хотя рукоприкладство было исключительной редкостью у поздних Романовых.[1]
Образование
У братьев были одни преподаватели, хотя учились они в разных комнатах. Среди их наставников были самые уважаемые профессора.[2] Оба брата в совершенстве владели английским языком, свободно говорили на французском и немецком, сносно изъяснялись на датском. Увлекались мальчики стрельбой и рыбалкой. Георгию прочили карьеру на флоте, пока он не заболел туберкулёзом.
По решению родителей в 1890 году Георгий вместе со старшим братом отправился в заграничное путешествие, конечной точкой которого должна была стать Япония. Мария Фёдоровна надеялась, что солнце и морской воздух пойдут сыну на пользу. Однако примерно на полпути, в Бомбее, с Георгием случился приступ, и он был вынужден вернуться обратно. Николай продолжил путешествие без брата.
Наследник Цесаревич[%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C | править вики-текст] В 1894 году неожиданно умер Александр III. Николай стал императором. Поскольку детей у него ещё не было, наследником цесаревичем был объявлен Георгий.
Однако состояние здоровья Георгия оставалось плохим. Он жил на Кавказе, в Абастумани. Врачи даже запретили ему ехать в Петербург на похороны отца (хотя он присутствовал при кончине отца в Ливадии). Единственной радостью Георгия были визиты матери. В 1895 году они вместе ездили к родственникам в Данию. Там с ним случился очередной приступ. Георгий долгое время был прикован к постели, пока наконец не почувствовал себя лучше и не вернулся в Абастумани.
Манифест императора Александра Второго о рождении Георгия Александровича Сын императора Александра III великий князь Георгий Александрови.jpg Награды[%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C | править вики-текст] российские:
Орден Святого апостола Андрея Первозванного (27.04.1871) Орден Святого Александра Невского (27.04.1871) Орден Белого орла (27.04.1871) Орден Святой Анны 1-й ст. (27.04.1871) иностранные:
Австрийский орден Святого Стефана большой крест (1885) Испанский орден Золотого руна (1896) Итальянский орден Благовещения (1890) Греческий орден Спасителя 5-й ст. Смерть и погребение[%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C | править вики-текст] 28 июня 1899 года, в возрасте 28 лет, скоропостижно скончался по дороге от Зекарского перевала обратно в Абас-Туман «на велосипеде с бензиновым двигателем» на глазах у молоканки Анны Дасаевой — согласно официальному извещению в правительственной газете[3].
Великий князь Георгий Александрович за письменным столом. Абастумани. 1890-е гг. Весть о смерти Георгия была тяжёлым ударом для всей императорской семьи и особенно для Марии Феодоровны.
Погребение его совершалось по Высочайше утверждённому церемониалу[4]: останки были доставлены в Боржоми на колеснице, затем поездом по железной дороге в Батум, далее на эскадренном броненосце «Георгий Победоносец» в Новороссийск, откуда поездом — в Санкт-Петербург, куда гроб с его телом прибыл 12 июля и поставлен в Петропавловском соборе[5]. Отпевание 14 июля возглавил митрополит Санкт-Петербургский Антоний (Вадковский), присутствовали император и императрица[6]; похоронен в Петропавловском соборе рядом с саркофагом отца.
Память[%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C | править вики-текст] Николай всегда помнил Георгия и особенно его замечательное чувство юмора. Он записывал лучшие шутки брата на клочках бумаги и собирал их в «шкатулку курьезов». И годы спустя царь не раз использовал её, чтобы позабавить близких. В 1910 году младший брат Георгия Михаил, в память о брате дал своему новорождённому сыну имя Георгий. Георгий Михайлович также прожил недолго и погиб в автокатастрофе в 1931 году.
В честь князя было названо основанное в 1885 году немецкими колонистами поселение Георгсфельд в Закавказье (в наст. время — пос. Чинарлы в Азербайджане)
В 1994 году тело цесаревича Георгия эксгумировалось для анализа ДНК и сравнения её с ДНК останков царской семьи (см. Романовы#Генетические исследования). Это решило многолетнюю проблему нахождения ДНК ближайших родственников последнего императора (зарубежные потомки отказывались предоставить материал). «С медицинской, научной, криминалистической, наконец, точек зрения результат был превосходный. Полное совпадение генотипа Георгия Александровича с генотипом так называемого „скелета № 4“ (под таким номером значились останки Николая II), включая даже тот сдвоенный элемент в ДНК»[7].
В культуре
Является одним из двух главных персонажей в цикле книг "Кавказский принц" Андрея Величко.Так же фигурирует в романе В.С. Пикуля "Нечистая сила".
Примечания
commons: Георгий Александрович на Викискладе? Wall С 1.11.1893 г. по 1.04.1895 г. Георгию в Абастумане читал курс всеобщей истории профессор В.О. Ключевский.//Нечкина М.В. Василий Осипович Ключевский. История жизни и творчества. М., 1974. - С.325, 330. «Правительственный Вѣстникъ». 3 (15) июля 1899, № 142, стр. 1. Церемоніалъ перевезенія тѣла Его Императорскаго Высочества въ Бозѣ почившаго Наслѣдника Цесаревича и Великаго Князя Георгія Александровича изъ Абасъ-Тумана, на Кавказѣ, въ С.-Петербургъ въ Петропавловскій соборъ и погребенія въ ономъ. // «Правительственный Вѣстникъ». 8 (20) июля 1899, № 146, стр. 1. «Правительственный Вѣстникъ». 13 (25) июля 1899, № 150, стр. 2. «Правительственный Вѣстникъ». 15 (27) июля 1899, № 152, стр. 2. «От Алексея и Марии осталось 60 граммов на двоих» // Культура Ссылки[%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C | править вики-текст] Георгий Александрович, сын Александра III // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
Абастумани и Российская императорская семья. Часть 4 Профиль Великого князя Георгия Александровича на официальном сайте РАН
| 1871 |
May 6, 1871
|
Tsarskoye Selo, Pushkin, gorod Sankt-Peterburg, Sankt-Peterburg, Russia (Russian Federation)
|
|
|
May 9, 1871
|
Alexander Palace, Pushkin, gorod Sankt-Peterburg, gorod Sankt-Peterburg, Russia (Russian Federation)
|
||
|
May 9, 1871
- November 1, 1894
|
Saint Petersburg, gorod Sankt-Peterburg, Saint Petersburg, Russia (Russian Federation)
|
||
| 1894 |
November 1, 1894
- August 8, 1899
Age 23
|
Saint Petersburg, gorod Sankt-Peterburg, Saint Petersburg, Russia (Russian Federation)
|
|
| 1899 |
August 9, 1899
Age 28
|
Bordżomi (formerly Abbas-Tuman), Szida Kartli, Georgia
|
|
|
August 14, 1899
Age 28
|
Peter and Paul, Cathedral, Russia, Санкт-Петербург (Sankt-Pietierburg), Russian Federation
|